Laravel Post View Counter: Monitor Your Content's Popularity
- Published on
- Jigar Patel--5 min read
Overview
- Introduction
- Step 1: Install Laravel
- Step 2: Create the Posts Table Using Migration
- Step 3: Create the Post Model
- Step 4: Create the Factory Class
- Step 5: Create Routes
- Step 6: Create the Controller
- Step 7: Create View Files
- Quick summary:
- Source Code
- About the Author
- We're Hiring
- Related Blogs

Introduction
In this tutorial, we will explore how to create a visitor counter or post view counter in Laravel. We will cover the entire process, including setting up a "posts" table with a "viewer count" column, creating a list of posts with a "view" button, and implementing the functionality to increment the visitor count when a user clicks the button. This tutorial will help you integrate a visitor counter into your Laravel website to track post views. It is compatible with Laravel versions 6 to 10.
Step 1: Install Laravel
If you haven't already created a Laravel application, you can do so by running the following command:
composer create-project laravel/laravel example-app
Step 2: Create the Posts Table Using Migration
To create a new migration for adding a posts table, execute the following command:
php artisan make:migration create_posts_table
In the generated migration file located in the database/migrations directory, add the following code to define the structure of the posts table:
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('title');
$table->string('slug');
$table->text('body');
$table->integer('viewer')->nullable();
$table->timestamps();
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('posts');
}
};
Next, run the migration to create the posts table:
php artisan migrate
Step 3: Create the Post Model
After creating the posts table, create the Post model to interact with the posts. Create a file named Post.php in the app/Models directory and add the following content to it:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Post extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
protected $fillable = ['title', 'body', 'slug', 'viewer'];
}
Step 4: Create the Factory Class
To generate dummy data for testing purposes, create a factory class for the Post model. Run the following command:
php artisan make:factory PostFactory --model=Post
In the generated PostFactory.php file located in the database/factories directory, add the following code to define the default state for generating posts:
<?php
namespace Database\Factories;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory;
use App\Models\Post;
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
class PostFactory extends Factory
{
protected $model = Post::class;
public function definition(): array
{
return [
'title' => $this->faker->text(),
'slug' => Str::slug($this->faker->text()),
'body' => $this->faker->paragraph(),
];
}
}
Generate test data by running the following commands in the terminal:
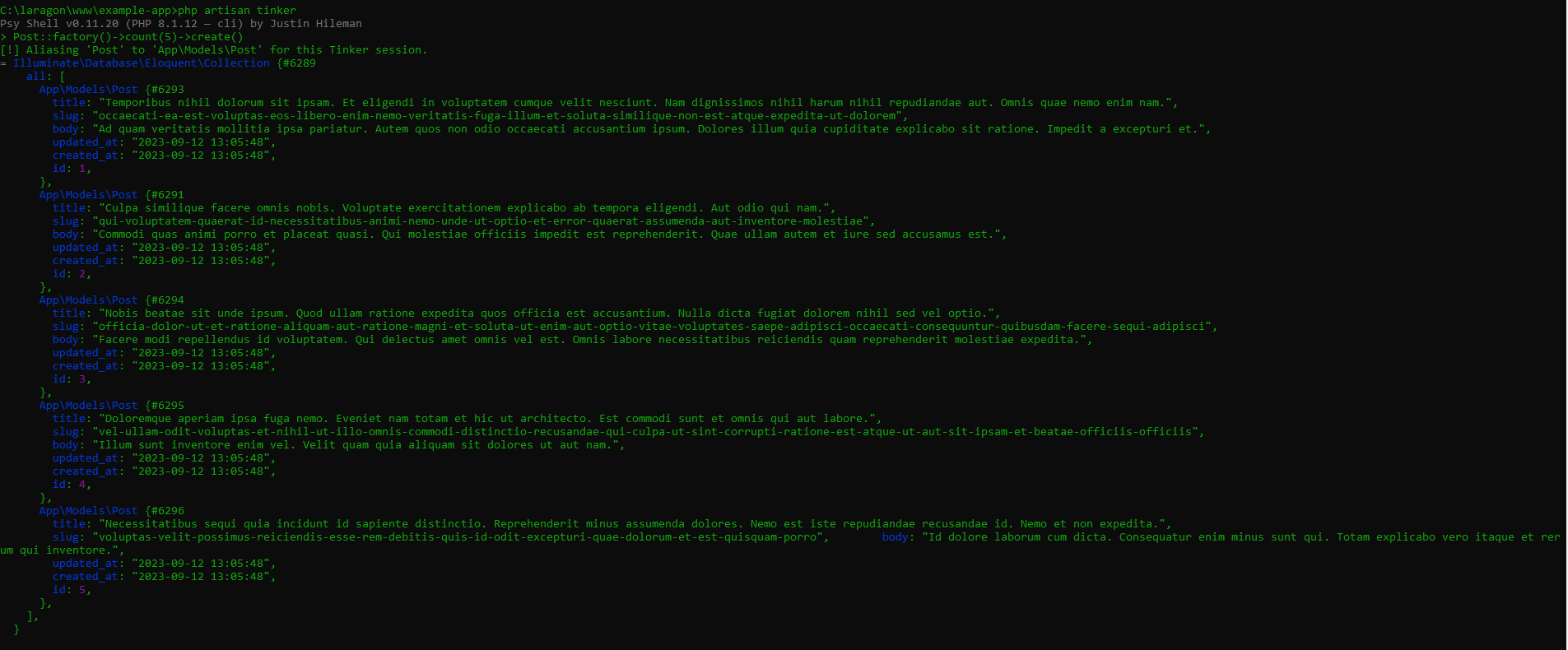
php artisan tinker
Post::factory()->count(5)->create()
Step 5: Create Routes
Define routes to display the list of posts and view a specific post. Open the routes/web.php file and add the following route definitions:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\PostController;
Route::get('posts', [PostController::class, 'index'])->name('posts.index');
Route::get('posts/{id}', [PostController::class, 'show'])->name('posts.show');
Step 6: Create the Controller
Create a new controller named PostController with methods for displaying posts and viewing a single post. Add the following code to the PostController.php file:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\Post;
class PostController extends Controller
{
public function index(Request $request)
{
$posts = Post::paginate(20);
return view('posts', compact('posts'));
}
public function show($id)
{
$post = Post::find($id);
$post->increment('viewer');
return view('postShow', compact('post'));
}
}
Step 7: Create View Files
Create Blade view files for displaying the list of posts and viewing a single post. Create posts.blade.php and postShow.blade.php in the resources/views directory with the following content:
posts.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="{{ str_replace('_', '-', app()->getLocale()) }}">
<head>
<meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}" />
<title>Laravel Post View Count Tutorial - ItSolutionStuff.com</title>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.0-beta1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5" style="max-width: 750px">
<h1>Laravel Post View Count Tutorial - ItSolutionStuff.com</h1>
<div id="data-wrapper">
@foreach ($posts as $post)
<div class="card mb-2">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{ $post->title }}</h5>
{!! Str::limit($post->body, 100) !!}
<br />
<a href="{{ route('posts.show', $post->id) }}">View</a>
</div>
</div>
@endforeach
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
postShow.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="{{ str_replace('_', '-', app()->getLocale()) }}">
<head>
<meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}" />
<title>Laravel Post View Count Tutorial - ItSolutionStuff.com</title>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.0-beta1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<h1>{{ $post->title }} - ItSolutionStuff.com</h1>
<strong class="text-danger">Total Views: {{ $post->viewer }}</strong>
<p>{!! $post->body !!}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
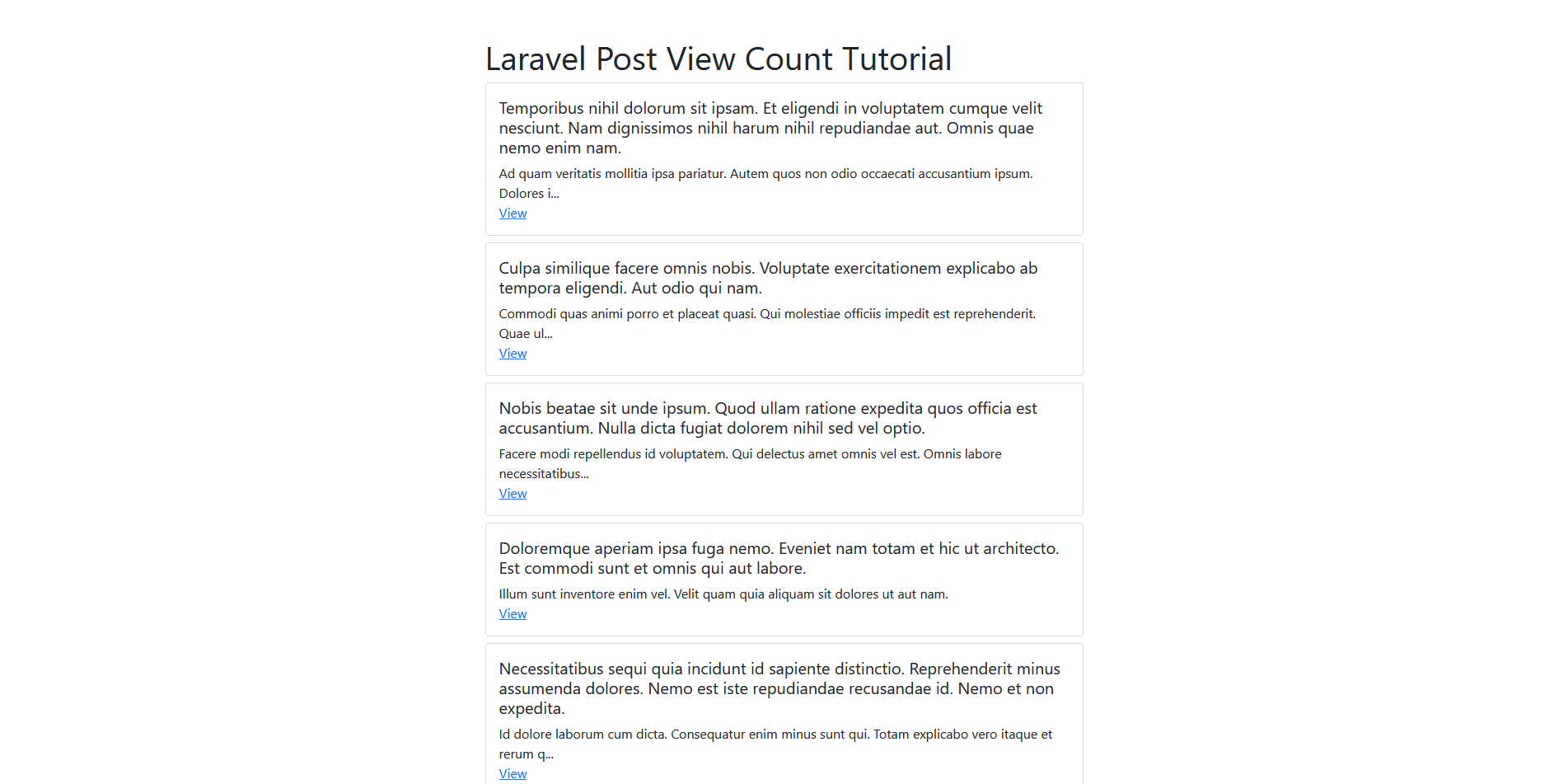
Running the Laravel App: To run the Laravel app, use the following command:
php artisan serve
Open your web browser and access the following URL to view the app:
http://localhost:8000/posts
Output:

Quick summary:
By following these steps, you can successfully implement a visitor counter or post view counter in your Laravel application. This tutorial covers setting up the database, creating models, controllers, routes, and views to achieve this functionality.
Source Code
The complete source code for this tutorial is available on GitHub. You can find it Here.
About the Author
Jigar Patel is a React.js enthusiast and a software developer at JBCodeapp Company. Visit our JBCodeapp to learn more about our work in the React.js ecosystem.
We're Hiring
Are you passionate about React.js development? We're always on the lookout for talented developers to join our team. Check out our careers page for current job openings.